
Understanding and treating pigment spots
How are pigments formed in the skin?
The pigmentation of the skin is the consequence of the production of melanin. This phenomenon is called melanogenesis.
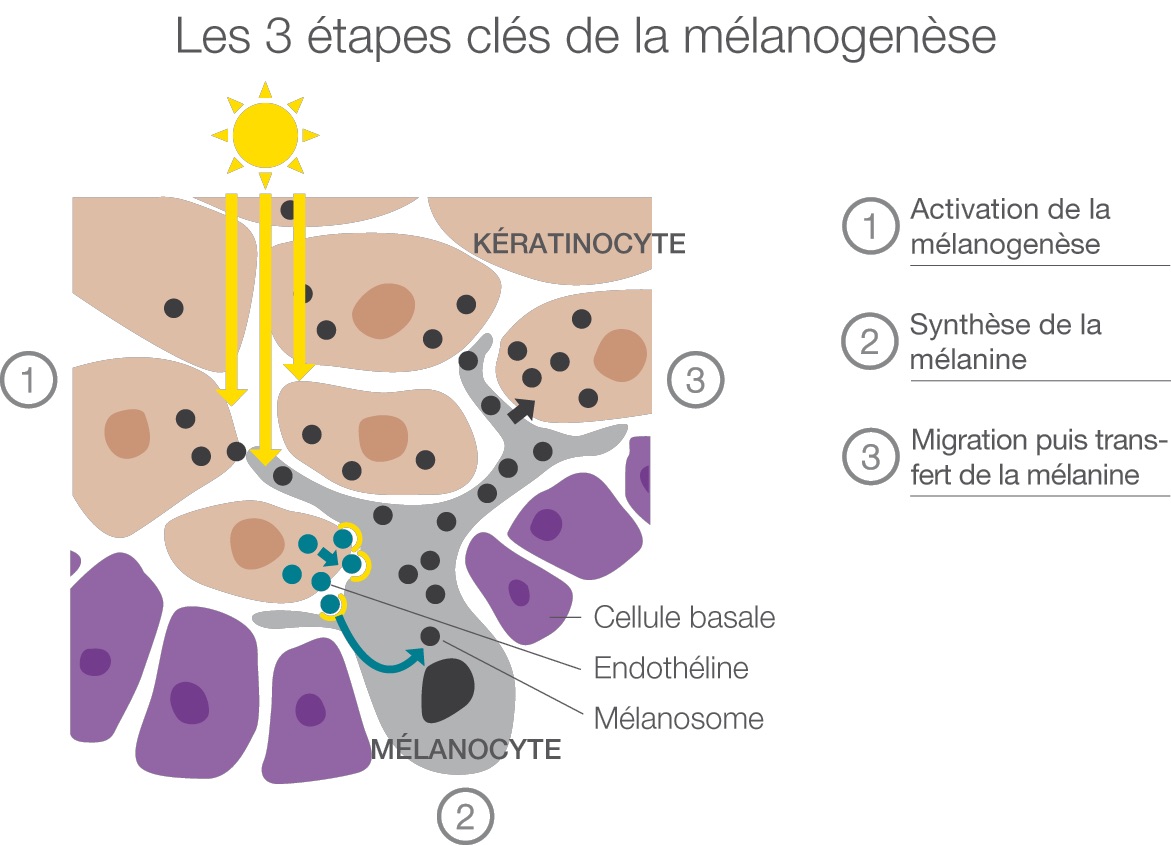
The cells responsible for the production of melanin are the melanocytesThey are located at the base of the epidermis (the most superficial layer of the skin). They are evenly distributed in the basal layer of the epidermis and in the hair follicles. The number of melanocytes is identical in the different ethnic skin types. Each melanocyte is in relation with about 36 keratinocytes, to which it distributes the melanin produced, thus forming an "epidermal melanisation unit".
In the drawing opposite, the grey cell is a melanocyte. The cells surrounding it (in beige) are the keratinocytesThe main cells of the epidermis. When melanin is produced, it is transferred to all the neighbouring cells. The pigment thus spreads to the base of the epidermis, giving the skin its brown colouring.
There are two types of melanins:
- The eumelanins brown or black in colour (predominantly dark skinned)
- The pheomelanins yellow or reddish-orange, less photoprotective (most common in red skin).
This is how skin colours range from very light to black. The red colour is due to the presence of a particular melanin of different colour.
Melanin pigmentation is therefore genetically determined, and is UV-regulatedsome hormones and chemical mediators. The ultraviolet rays of the sun cause an increase in the activity of melanocytes: the skin turns brown, this is what we call the tanning. It is a way for the epidermis to protect itself.
What are the different types of pigmented spots?
There are different types of spots of melanic origin:
The beauty spotsThese are benign proliferations of melanocytes that gather in clusters. They obviously do not fall within the scope of depigmenting cosmetic products.
The freckles are small spots made of this particular melanin that only redheaded skin produces. They are natural and become more visible in the sun.
The sun spots or age spots (which dermatologists call lentigo)
 are small dark brown spots that are more common on parts of the body exposed to the sun (back of the hands, neckline, face). The pigment sits at the base of the epidermis. They increase in size and number with age. They are the preferred target of depigmenting cosmetics.
are small dark brown spots that are more common on parts of the body exposed to the sun (back of the hands, neckline, face). The pigment sits at the base of the epidermis. They increase in size and number with age. They are the preferred target of depigmenting cosmetics.
The melasma peut apparaître durant la grossesse ou lors d’un traitement hormonal (pilule). Il est accentué par le sun. They are light brown to very dark brown spots with irregular borders. They are located on the forehead, cheeks and sometimes the upper lip, in a symmetrical way. The melanin pigment may be located in the epidermis, but also in the dermis or in both locations at the same time. Only the pigment present in the epidermis can be improved by depigmenting cosmetics.
The post-inflammatory pigmented marks are the pigmented after-effects of an inflammation of the skin. They can occur after an infection, a skin allergy, a reaction to medication or trauma. They are frequent during acne.
How do depigmenting products work?
The depigmenting productsanti-spot, or lightening, allow to reduce the intensity of the pigmentbut do not make the spots disappear completely. Three main mechanisms allow the reduction of pigmented spots: reduction of the triggering signals caused by the sun's ultraviolet rays, reduction of the production of melanin in the melanocytes, reduction of the transfer of melanin to the cells of the epidermis.




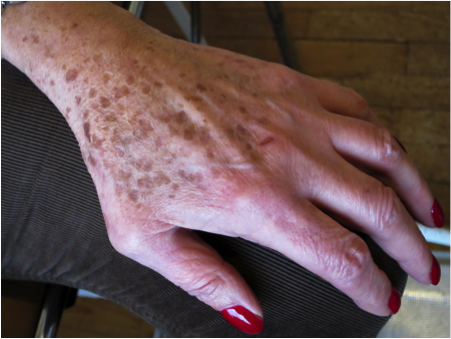 are small dark brown spots that are more common on parts of the body exposed to the sun (back of the hands, neckline, face). The pigment sits at the base of the epidermis. They increase in size and number with age. They are the preferred target of
are small dark brown spots that are more common on parts of the body exposed to the sun (back of the hands, neckline, face). The pigment sits at the base of the epidermis. They increase in size and number with age. They are the preferred target of 